what is the best way to describe co-teaching?
Teaching Methods
The termteaching method refers to the general principles, didactics and management strategies used for classroom pedagogy.
Your choice of teaching method depends on what fits you — your educational philosophy, classroom demographic, subject(s) and school mission statement.
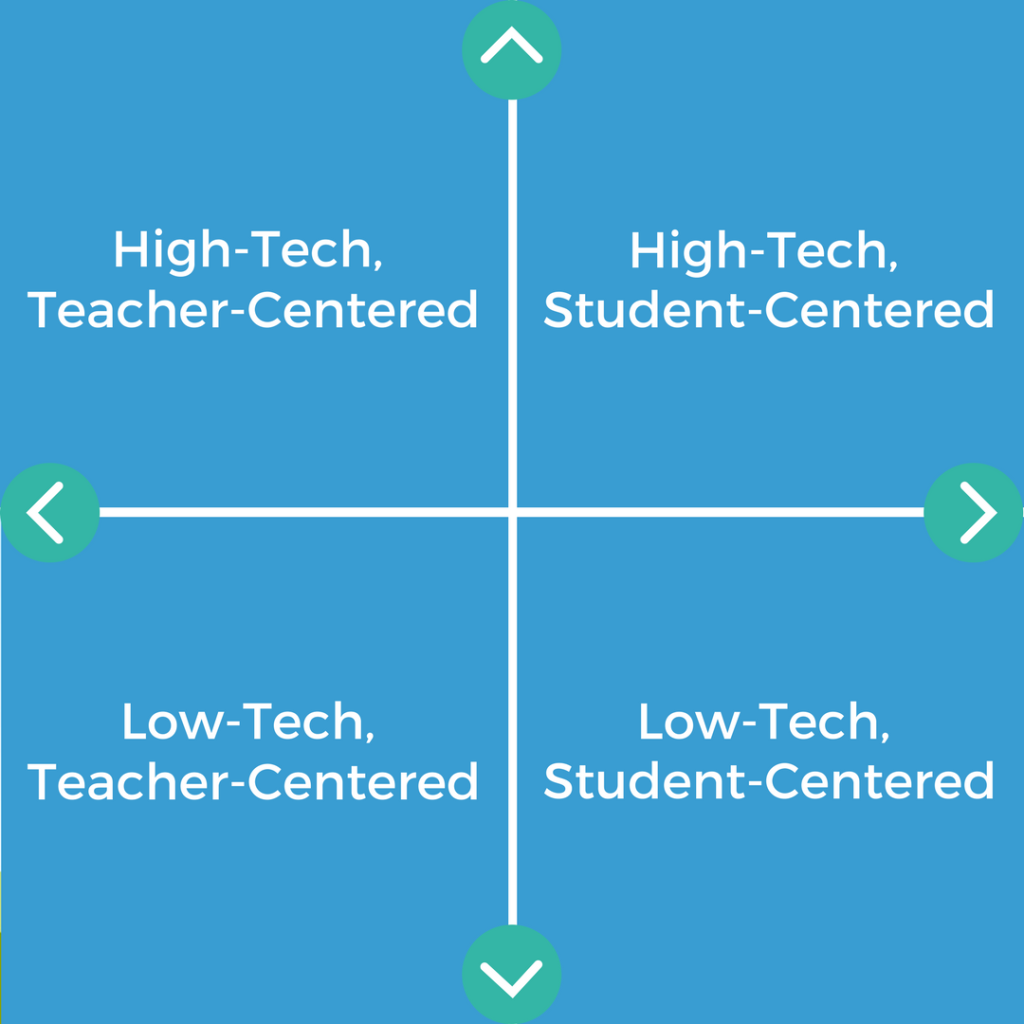
Teaching theories can be organized into 4 categories based on two major parameters: a teacher-centered approach versus a pupil-centered approach, and high-tech material use versus depression-tech material use.
Interested in developing your skills equally a teacher? Explore online education short courses designed to give you an in depth understanding of various skills in education.
Instructor-Centered Approach to Learning
Taken to its most farthermost interpretation, teachers are the main authority effigy in a teacher-centered education model. Students are viewed as "empty vessels" who passively receive knowledge from their teachers through lectures and direct didactics, with an end goal of positive results from testing and assessment. In this way, educational activity and assessment are viewed as 2 split up entities; educatee learning is measured through objectively scored tests and assessments.
Learn more near the dissimilar teaching styles that apply a teacher-centered arroyo.
Student-Centered Approach to Learning
While teachers are even so an potency effigy in a student-centered pedagogy model, teachers and students play an equally active function in the learning process.
The teacher's master role is to coach and facilitate educatee learning and overall comprehension of fabric, and to measure student learning through both formal and informal forms of assessment, like group projects, student portfolios, and class participation. In the educatee-centered classroom, teaching and assessment are connected because student learning is continuously measured during instructor instruction.
Learn more about the unlike teaching styles that use a pupil-centered approach.
Loftier Tech Approach to Learning
Advancements in applied science have propelled the education sector in the concluding few decades. Every bit the name suggests, the high tech approach to learning utilizes unlike engineering to aid students in their classroom learning. Many educators use computers and tablets in the classroom, and others may utilize the net to assign homework. The internet is also benign in a classroom setting every bit it provides unlimited resources. Teachers may likewise utilize the internet in guild to connect their students with people from around the world.
Below are some tech tools used in classrooms today:
- Yard Suite (Gmail, Docs, Sheets, Classroom, Drive, and Calendar)
- Tablets/laptops
- Gamification software (such as 3DGameLab and Classcraft)
- Educational activity-focused social media platforms (such every bit schoology and seesaw)
- Engineering accessibility for students with disabilities
Derek Bok Center for Teaching and Learning
Higher Education Teaching Certificate
Deepen your understanding of college-order educational activity practices and augment your skill set while creating a unique and inclusive strategy for your specific context.
School of Educational activity and Health Sciences
Master of Science in Education in Educational Leadership
No GRE scores are required to apply to University of Dayton's online MSE in Educational Leadership programme. The plan is thirty credits and can be completed in two years with the completion of an internship.
- Optional path to primary licensure runway
- No GRE required to apply
- Degree can be completed in as few as two years
Depression Tech Approach to Learning
While applied science undoubtedly has changed education, many educators opt to apply a more than traditional, low tech arroyo to learning. Some learning styles require a physical presence and interaction between the educator and the student. Additionally, some research has shown that low-tech classrooms may boost learning. For example, students who accept handwritten notes accept meliorate recall than students who accept typed notes. Another downside of technology in the classroom may exist that students exposed to spell cheque and autocorrect features at an before historic period may be weaker in spelling and writing skills. Ultimately, tailoring the learning experience to different types of learners is incredibly important, and sometimes students work ameliorate with a low-tech approach.
Here are some examples of low applied science usage in different teaching methodologies:
- Kinesthetic learners have a demand for movement when learning. Teachers should allow students to move around, speak with hands and gestures.
- Expeditionary learning involves "learning past doing" and participating in a easily-on experience. Students may participate in fieldwork, learning expeditions, projects or case studies to be able to apply knowledge learned in the classroom to the real earth, rather than learning through the virtual world.
- Many types of vocational or applied training cannot exist learned virtually, whether it exist a laboratory experiment or woodworking.
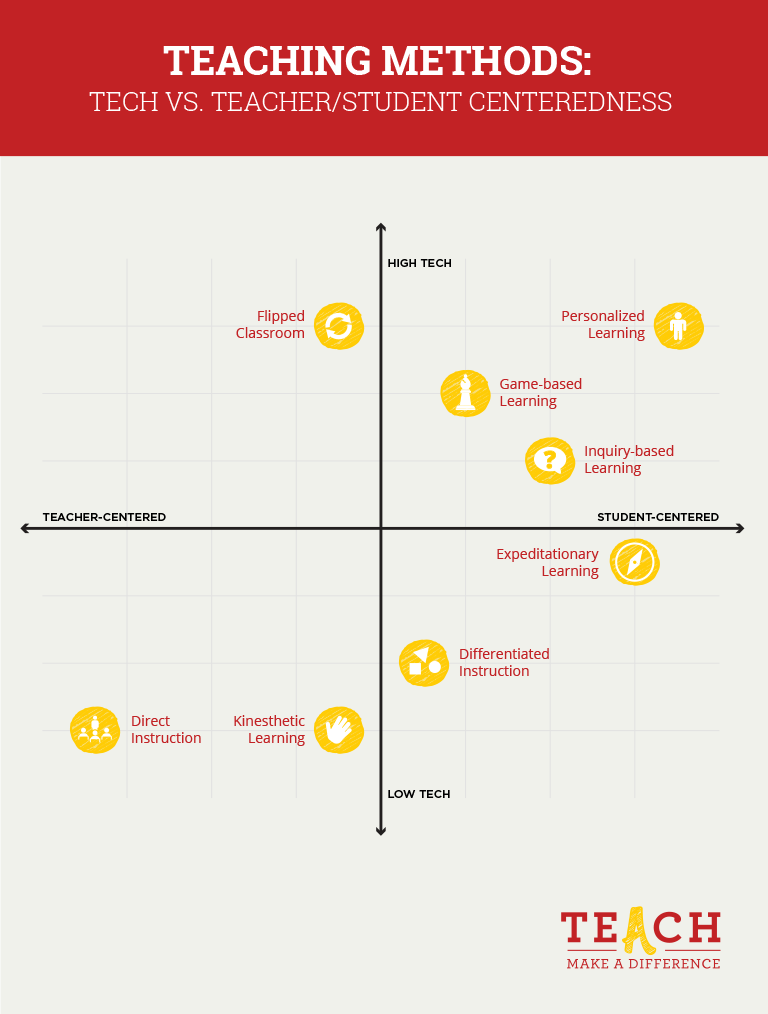
Through these dissimilar approaches to teaching, educators can gain a better understanding of how all-time to govern their classrooms, implement instruction, and connect with their students. Inside each category of teacher and student centeredness and tech usage, there are specific teaching roles or "methods" of instructor behavior that characteristic their ain unique mix of learning and assessment practices. Larn more than nearly each one to discover the best fit for your classroom.
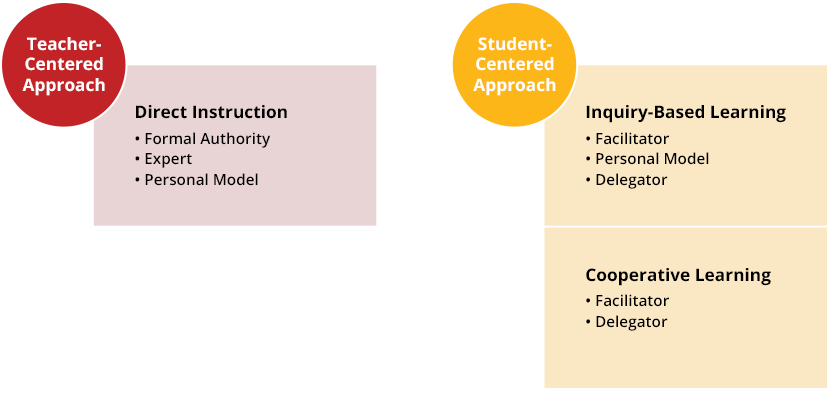
Teacher-Centered Methods of Pedagogy
Direct educational activity is the general term that refers to the traditional teaching strategy that relies on explicit teaching through lectures and instructor-led demonstrations.
In this method of educational activity, the teacher might play one or all of the following roles:
Formal Potency teachers are in a position of power and authorization because of their exemplary knowledge and status over their students. Classroom direction styles are traditional and focus on rules and expectations.
Expert teachers are in possession of all knowledge and expertise inside the classroom. Their chief role is to guide and direct learners through the learning procedure. Students are viewed solely as the receptors of cognition and information ("empty vessels").
Teachers who operate under the "Personal Model' mode are those who lead by example, demonstrating to students how to admission and comprehend information. In this teaching model, students learn through observing and copying the teacher'southward procedure.
As the primary pedagogy strategy nether theinstructor-centered approach, direct instruction utilizes passive learning, or the idea that students tin can learn what they demand to through listening and watching very precise education. Teachers and professors act as the sole supplier of noesis, and nether the direct instruction model, teachers often utilize systematic, scripted lesson plans. Straight teaching programs include exactly what the teacher should say, and activities that students should complete, for every minute of the lesson.
Considering information technology does not include student preferences or requite them opportunities for hands-on or alternative types of learning, direct instruction is extremely teacher-centered. it's also adequately low-tech, ofttimes relying on the apply of textbooks and workbooks instead of computers and 1:i devices.
Back to Top
The thought of the flipped classroom began in 2007 when 2 teachers began using software that would allow them record their live lectures. By the next school year, they were implementing pre-recorded lectures and sharing the idea of what became known equally the flipped classroom.
Broadly, the flipped classroom characterization describes the teaching structure that has students watching pre-recorded lessons at abode and completing in-grade assignments, as opposed to hearing lectures in form and doing homework at home. Teachers who implement the flipped classroom model often flick their own instructional videos, but many as well use pre-made videos from online sources.
A key benefit of the flipped classroom model is that it allows for students to work at their ain stride if that is how the teacher chooses to implement it. In some cases, teachers may assign the aforementioned videos to all students, while in others, teachers may choose to permit students to spotter new videos every bit they primary topics (taking on a more "differentiated" arroyo).
But despite this potential for more student-centeredness, flipped classroom models are even so generally based on a teacher's idea of how learning should happen and what information students need, making it importantly teacher-centered. From a applied science perspective, the arrangement hinges on pre-recorded lessons and online activities, meaning both students and teachers need a good net connectedness and devices that tin can access it.
Back to Top
Sometimes known as tactile learning"or "hands-on learning", kinesthetic learning is based on the idea of multiple intelligences External link , requiring students to practise, brand, or create. In a kinesthetic learning environment, students perform physical activities rather than listen to lectures or watch demonstrations. Hands-on experiences, cartoon, role-play, building, and the use of drama and sports are all examples of kinesthetic classroom activities.
Though a bang-up fashion to go along students engaged and, at times, simply awake, very few classrooms employ kinesthetic learning activities exclusively. One reason is that, despite the popularity of learning style theories, in that location is a lack of enquiry-based testify that shows that teaching to certain learning styles produces better academic results.
One upside is that kinesthetic learning is rarely based on technology, equally the method values movement and creativity over technological skills. That means information technology's cheap and fairly low-barrier to prefer, as well as a welcome pause from students' existing screen time. Kinesthetic learning can be more than student-centered than teacher-centered when students are given the choice of how to utilise movement to learn new information or experience new skills, and then it's likewise adaptable to a teacher'southward particular classroom preferences.
Read More:
- Using Classroom Debates to Engage Students
- The Benefits of Puzzles in Early Childhood
Back to Top
Student-Centered Methods of Didactics
Differentiated instruction is the educational activity practice of tailoring instruction to run into private pupil needs. It initially grew pop with the 1975 Individuals with Disabilities Instruction Human activity (Idea), which ensured all children had equal admission to public education. The Individualized Instruction Programs (IEPs) that started under IDEA helped classroom teachers differentiate for students with special needs. Today, differentiated instruction is used to encounter the needs of all types of learners.
Teachers can differentiate in a number of ways: how students access content, the types of activities students do to master a concept, what the end product of learning looks like, and how the classroom is set. Some examples of differentiation include: having students read books at their own reading levels, offering different spelling lists to students, or meeting in small groups to reteach topics.
Though differentiation is focused on individual student needs, information technology is mostly planned and implemented past the teacher. And engineering science, though a potential assist, is not a authentication of the differentiated teaching fashion, making it a fairly traditional, low-barrier method to prefer.
Read More:
- Engaging Gifted and Talented Students
- How to Appoint a Classroom of Diverse Learners
- Become a Gifted Education Teacher
Dorsum to Tiptop
Based on student investigation and hands-on projects, research-based learning is a teaching method that casts a instructor as a supportive figure who provides guidance and support for students throughout their learning process, rather than a sole potency figure.
In this method of instruction, the teacher might play one or all of the post-obit roles:
Facilitators play a potent emphasis on the teacher-student relationship. Operating under an open classroom model, in that location is a de-emphasis on teacher instruction, and both student and educator undergo the learning process together. Pupil learning loosely guided by the teacher, and is focused on fostering independence, hands-on learning, and exploration.
Teachers who operate nether the "Personal Model" style are those who lead by example, demonstrating to students how to access and comprehend information. In this instruction model, students learn through observing and copying the teacher's process.
Teachers acts as a "resource" to students, answering questions and reviewing their progress every bit needed. Teachers play a passive role in student's learning; students are active and engaged participants in their learning. The main goal of a Delegator is to foster a sense of autonomy in the learning process.
Teachers encourage students to ask questions and consider what they want to know nearly the world around them. Students then enquiry their questions, find information and sources that explicate central concepts and solve bug they may encounter along the way. Findings might be presented as self-made videos, websites, or formal presentations of research results.
Inquiry-based learning falls under the student-centered arroyo, in that students play an active and participatory function in their own learning. Only teacher facilitation is likewise extremely key to the process. Usually, during the inquiry cycle, every student is working on a unlike question or topic. In this environment, teachers ask loftier-level questions and make research suggestions nearly the process rather than the content. At the cease of the inquiry cycle, students reflect on the experience and what they learned. They also consider how information technology connects to other topics of interest, as an inquiry on one topic ofttimes results in more questions and so an inquiry into new fields.
Inquiry-based learning tin can make not bad use of applied science through online research sites, social media, and the possibility for global connections with people outside of the community. Only depending on the subject at hand, it doesn't necessarily crave information technology.
Read More:
- 9 Maker Projects for Beginner Maker Ed Teachers
Back to Height
Expeditionary learning is based on the ideas of the educator who founded Outward Bound, and is a form of project-based learning in which students proceed expeditions and appoint in in-depth written report of topics that impact their schools and communities.
The learning in this model includes multiple content areas so that students can run into how problem-solving can happen in the real world–ideally, their ain worlds. A student in a big city, for example, might study statistics virtually pollution, read information nigh its effects, and travel to sites in their city that have been impacted by the problem. When they have a good understanding of the circumstances, students and teachers work to notice a solution they can actively implement.
Technology-wise, 1000 Suite (Google Docs, Sheets, and Bulldoze) and cyberspace access tin aid pupil enquiry, presentation, and implementation of projects. But it's the easily-on work and getting out into the community that's the cornerstone of this methodology.
Back to Tiptop
Personalized learning is such a new educational model that its definition is yet evolving. At the heart of the model, teachers accept students follow personalized learning plans that are specific to their interests and skills. Student cocky-management and selection in the curriculum are hallmarks of personalized learning.
Assessment is likewise tailored to the individual: schools and classrooms that implement personalized learning utilise competency-based progression, so that students tin move onto the next standards or topics when they've mastered what they're currently working on. That way, students in personalized learning classrooms tin can progress to work across their grade level equally they main topics, while students who demand additional assist have that time built into their daily schedules every bit well.
In that location's also room for an emphasis on college and career readiness in personalized learning environments. Students who don't require remediation or extension work can instead work with teachers to nurture social skills and other or 21st-century skills lessons and receive mentoring.
Personalized learning is extremely student centered, merely teachers are required to teach lessons, look at frequent assessment data, and meet with students to make any necessary changes to their learning plans. They'll also need to have a certain comfort level with engineering science: the differentiated and personalized instruction that students receive often come up in the form of online lessons and programs, so teachers must exist able to navigate virtual platforms with ease.
Read More
- How Technology Changed the Way I Teach My Students
Back to Top
Game-based learning comes from the want to engage students in more agile learning in the classroom. Considering they require students to be problem solvers and employ soft skills that they will need as adults, games are a great style to encourage a "mastery" mindset, rather than a focus on grades.
In a game-based learning environment, students piece of work on quests to reach a specific goal (learning objective) by choosing actions and experimenting forth the way. Equally students make certain progress or achievements, they can earn badges and experience points, just similar they would in their favorite video games.
Game-based learning requires a lot of fourth dimension and planning on the teachers' office. Fortunately, at that place is software that makes this process much easier, similar 3DGameLab and Classcraft. Teachers who use this software may be better at differentiating quests for students because of the data the programs provide.
Because teachers play a big role in planning and creating content under this model, game-based learning isn't completely pupil-centered. Just it is still very much focused on the student, who works at their own footstep and makes independent choices in a gamified environs.
Back to Top
Last Updated Baronial 2020
Source: https://teach.com/what/teachers-know/teaching-methods/
0 Response to "what is the best way to describe co-teaching?"
إرسال تعليق